Fale sobre uma coisa complexa a fazer: instalar o Windows pela rede. Mesmo instalá-lo através de uma unidade USB(USB drive) é mais simples. No entanto, isso não significa que não possa ser feito. Usando uma ferramenta gratuita chamada Serva e um pouco de tempo e atenção(time and attention) , qualquer pessoa pode configurar seu ambiente de rede(network environment) para que as instalações do Windows(Windows) sejam realizadas com facilidade, a partir de um computador em rede(network computer) . Veja como funciona todo o processo!
Pré-requisitos MUITO IMPORTANTES
Há muitas coisas que você precisa preparar com antecedência, para que tudo funcione sem problemas. Por favor(Please) , não pule nenhum desses elementos ou a probabilidade de falha será alta:
You need to download and extract a little tool named Serva. Download the appropriate version for your operating system (32-bit or 64-bit). You will notice that there are a "Non-Supporter" version and a "Supporter" version. The free one is the "Non-Supporter" version. It includes a small annoyance when you start it, plus a few limitations that won't impact you unless you are a network admin or IT professional who needs to install lots of operating systems on many network computers. If you are such a professional, go ahead and purchase the "Supporter" version which costs a fair $29.99.
"D:SERVA"
You need the original installation files for the operating system(s) you want to install over the network. Have them at hand as you will need to copy them to a special folder, as they are, without modifications.
For the computers where you are about to install Windows over the network, identify their exact network card model(s). Then, download the appropriate drivers for the Windows version you are about to install on them. By default, Windows setup programs support a limited number of network cards. If your system is rather new, then it is very likely that it won't support its network card and the installation procedure will fail.
Every time you run Serva, run it as administrator. This way it has the required permissions to create files, save the settings you make, etc.
When you run Serva, make sure that it is not blocked by your firewall. The application must be set as allowed on the computer where it runs, otherwise it won't be able to transfer anything over the network.
The computer where the installation files are stored and the one where you want to install Windows must be part of the same network. This means that you have a router on your home network, managing network IP addresses and network traffic. If not, then you should directly connect the two computers with a crossover cable.
Etapa 1(Step 1) - Execute o Serva e faça(Run Serva & Make) sua configuração inicial(Initial Configuration)
Execute o Serva(Run Serva) como administrador. A versão gratuita pedirá que você espere 7 segundos antes de poder usá-la. Quando a espera terminar, clique em "Obrigado, hoje não"("Thanks, not today") .
Sua janela agora está aberta. Clique em Configurações(Settings) .

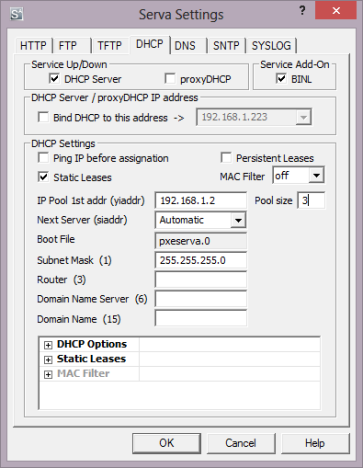
Primeiro, vá para a guia DHCP . Se seus computadores fazem parte da mesma rede e o gerenciamento de endereços IP(IP Addresses) é feito pelo seu roteador, habilite estas configurações: proxyDHCP e BINL .
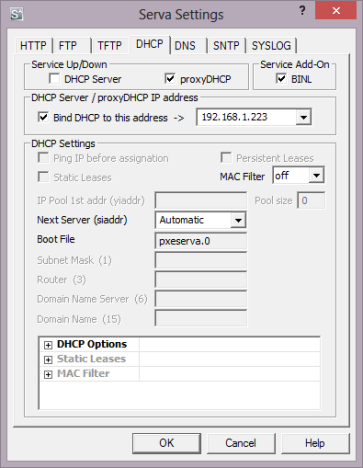
BINL é um add-on especial que atua como uma extensão do protocolo DHCP(DHCP protocol) e é usado pelo Serva durante seus procedimentos de preparação e manutenção(preparation and maintenance procedures) . proxyDHCP é uma configuração especial que informa ao Serva que ele não precisa agir como um servidor DCHP(DCHP server) para fornecer endereços IP aos computadores que se conectam a ele.
Embora os desenvolvedores do Serva não recomendem habilitar essa configuração, aprendemos em nossos testes que ela ajuda a eliminar alguns problemas. Portanto(Therefore) , ative também a caixa que diz "Ligar DHCP a este endereço" e deixe o ("Bind DHCP to this address")endereço IP(IP address) padrão fornecido.

Não há necessidade de modificar outras configurações nesta guia. Em seguida(Next) , vá para a guia TFTP .
O TFTP vem do Trivial File Transfer Protocol e é o protocolo usado pelo Serva para transferir arquivos pela rede. Este protocolo também precisa de um pouco de configuração.
Primeiro, marque a caixa próxima ao Servidor TFTP(TFTP Server) . Então, você precisa especificar o chamado diretório "raiz". Este é o diretório onde você planeja armazenar os arquivos de instalação do Windows . (Windows installation)Esta pasta pode ser a mesma pasta onde você extraiu o Serva ou uma nova. Tenha em mente que você deve usar caminhos curtos e evitar usar espaços e caracteres especiais (*, &, ", etc) no nome do diretório(directory name) ou em seu caminho.
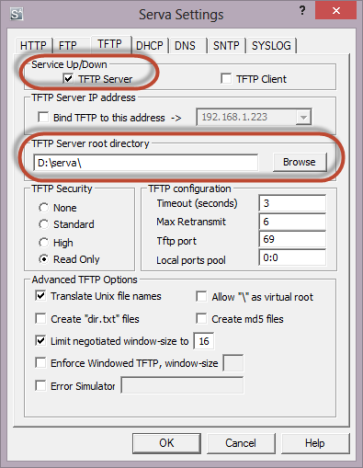
Para ajudar a eliminar problemas em alguns ambientes de rede, você também pode marcar a caixa ao lado de "Ligar TFTP a este endereço" e deixar o ("Bind TFTP to this address")endereço IP(IP address) padrão inalterado.

Pressione OK para salvar suas configurações. Em seguida, feche o Serva e inicie-o novamente (como administrador). Durante a reinicialização, ele criará uma estrutura(folder structure) de pastas especial na pasta raiz(root folder) que você especificou.
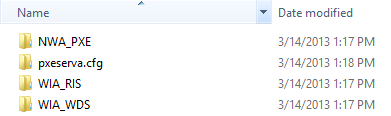
Entre(Amongst) essas pastas, você deve encontrar uma chamada WIA_WDS e outra chamada WIA_RIS . Se eles não forem encontrados na pasta raiz(root folder) que você especificou, algo deu errado com a configuração do Serva . Se tudo estiver bem, vá em frente e leia a próxima seção deste artigo.
Etapa 2(Step 2) - Copie os arquivos de instalação do Windows(Windows Installation Files)
Vá para a pasta raiz(root folder) que você especificou. Aqui, você precisa copiar os arquivos de instalação do Windows(Windows installation) , como estão, sem nenhuma modificação do seu lado.
Se você deseja instalar versões mais antigas do Windows , como Windows XP ou Windows(Windows XP or Windows) 2000, você precisa copiar esses arquivos na pasta WIA_RIS . Como esses sistemas operacionais são muito antigos e não recomendamos usá-los, não forneceremos instruções específicas para eles.
Se você planeja instalar o Windows Vista(Windows Vista) , Windows 7 ou Windows 8 , abra a pasta WIA_WDS . Lá, crie uma nova pasta nomeada de acordo com a versão do Windows(Windows version) que você deseja copiar. Use nomes de pastas simples, sem espaços ou caracteres especiais. Por exemplo, usei Windows_7 .
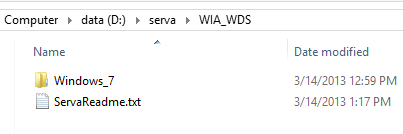
Crie(Create) pastas separadas, com nomes diferentes para todas as versões do Windows que você planeja instalar pela rede, usando Serva .
Dentro dessa pasta, copie e cole(copy and paste) todos os arquivos de instalação da versão do Windows(Windows version) que você deseja instalar pela rede. Basta(Simply) ir à raiz do disco de instalação(installation disc) e copiar toda a estrutura de arquivos e pastas(file and folder structure) .
Etapa 3 - Iniciar o Serva
Inicie o Serva(Start Serva) novamente, como administrador e espere(administrator and wait) que ele detecte os arquivos de instalação que você adicionou. Ele criará sua estrutura de pastas(folder structure) especial , necessária para distribuir os arquivos de instalação pela rede.
Em seguida, feche o Serva e vá para a próxima etapa.
Etapa 4(Step 4) - Copie o (s) driver(Network Card Driver) (s) da placa de rede
Em seguida, você precisa copiar os drivers da placa de rede(network card) do(s) computador(es) em que deseja instalar o Windows(Windows) .
Vá para a pasta onde você copiou os arquivos de instalação. No meu caso, era "D:serva" (tanto a pasta de instalação raiz quanto a do Serva(root and Serva installation folder) ), seguido por "WIA_WDSWindows_7" .

Lá, vá para "$OEM$$1DriversNIC" . Se você não conseguir encontrar essas pastas, crie-as você mesmo.
Em seguida, extraia os drivers da placa de rede e coloque-os dentro. (network card)Se seus drivers vierem como um setup.exe ou como um arquivo auto-extraível, extraia-o primeiro. Certifique-se de que os arquivos ".inf" e ".cat" do driver estejam armazenados diretamente na pasta NIC(NIC folder) .
Etapa 5(Step 5) - Compartilhe a pasta WIA_WDS(WIA_WDS Folder) com a rede
Para que o Serva distribua os arquivos de instalação do Windows(Windows installation) pela rede, eles precisam ser compartilhados com a rede, para que outros computadores possam acessá-los. Infelizmente, o Serva exige que você compartilhe a pasta WIA_WDS (e não suas subpastas ou outras pastas) usando um nome de compartilhamento(share name) muito específico : WIA_WDS_SHARE . Usar qualquer outro nome de compartilhamento(share name) significa que o procedimento de instalação(installation procedure) provavelmente falhará.

Para compartilhar esta pasta com o nome que mencionamos, primeiro você precisa habilitar o compartilhamento avançado no Windows e depois compartilhá-lo. Veja como funciona o compartilhamento avançado no Windows : Compartilhe bibliotecas ou pastas usando o compartilhamento avançado(Advanced Sharing) .
Você deve conceder permissões somente leitura ao usuário Todos . (Everyone)Você também pode compartilhar esta pasta com contas de usuário específicas, cujos detalhes de login você usará posteriormente, durante o processo de instalação da rede(network installation process) . Novamente(Again) , as permissões somente leitura são suficientes.
Etapa 6 - Iniciar o Serva
Inicie o Serva(Start Serva) novamente, usando permissões de administrador. Ele detectará os drivers de rede que você adicionou e fará algumas alterações, para que os drivers sejam distribuídos corretamente quando você iniciar o processo de instalação(installation process) em outros computadores. Agora você pode deixá-lo aberto e aguardando conexões de rede.
Em seguida, vá para o(s) computador(es) em que deseja instalar o Windows(Windows) .
Etapa 7(Step 7) - No PC de destino(Target PC) - Ative a inicialização da LAN e a inicialização(Lan Booting & Boot) da rede
Vá para o computador onde você deseja instalar o Windows(Windows) e entre em seu BIOS . Certifique(Make) -se de que a inicialização da rede esteja habilitada. Essa configuração pode ser chamada de "Boot from the network"("Boot from the network") ou "Boot from PXE" .
Em seguida, inicie o computador e pressione a tecla necessária para abrir o menu de inicialização(Boot Menu) . Na maioria dos computadores, você precisa pressionar F12 ou F8 , dependendo da versão do BIOS(BIOS version) . Selecione Rede(Network) ou PXE (novamente, isso depende do BIOS do seu computador ), para inicializar a partir da rede, usando Serva .

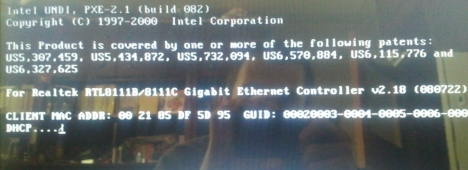
Se tudo estiver bem, você deverá ver uma tela parecida com a abaixo, onde é exibido o MAC do computador e a (MAC)placa de rede(network card) solicita um endereço IP(IP address) via DHCP .
Quando o computador está conectado à rede, o Serva carrega e exibe uma tela com os sistemas operacionais disponíveis para instalação. Escolha o que você deseja e pressione ENTER .

Os arquivos de instalação são carregados e uma pequena janela chamada ServaPENet é exibida. Nesta etapa, o Serva instala o driver de rede(network driver) adicionado anteriormente, carrega os recursos de rede e se conecta à pasta de instalação do Windows . (Windows installation)Dependendo de como você compartilhou a pasta WIA_WDS , ela solicitará que você forneça um nome de usuário e senha(username and password) para acessá-la. Digite os detalhes da conta de usuário(user account) com a qual você o compartilhou e conecte-se.
Se tudo correu bem, o processo de instalação do Windows(Windows installation) foi iniciado.
Etapa 8(Step 8) - Instalar o Windows pela rede
Em seguida, continue com a instalação do Windows(Windows installation) , como de costume. Se você planeja instalar o Windows 8(Windows 8) , consulte este guia de instalação(installation guide) : Como instalar o Windows 8 (Windows 8) RTM em seu computador(Your Computer) .
Solução de problemas com o Serva
Se você não prestar atenção a todas as etapas deste procedimento, é provável que algumas coisas falhem. Aqui estão algumas coisas que aprendemos ao experimentar esta ferramenta:
If ServaPENet returns this error: "Failed No NIC/Driver, Aborting!", it means that you forgot to copy the network card drivers as instructed at Step 4. If you copied them and you still get the error, double check that you have the correct driver for the network card of the computer where you want to install Windows, for the Windows version you are about to install. Also, double check that you copied it to the correct folder. Then, restart Serva to make sure it detects the driver before the network installation procedure starts.
If, on the target computer, Serva is not able to load at all over the network, consider enabling the "Bind DHCP to this address" and "Bind TFTP to this address" settings in the DHCP and TFTP tabs.
One last piece of advice is to check the Serva logs. The messages shown there can help you troubleshoot different problems.
Outra boa dica é reiniciar o Serva toda vez que você alterar alguma de suas configurações e toda vez que adicionar algo à sua pasta raiz(root folder) .
Como não somos os desenvolvedores deste software, não podemos fornecer suporte para ele e ajudá-lo com todos os problemas que você possa encontrar. Se nosso guia não ajudar você, verifique novamente a documentação do Serva - Serva PXE/BINL - AN01: Windows Install Guia de instalação do Windows e configuração avançada - Tópicos avançados em TFTP(Advanced Topics on TFTP) .
Conclusão
Como você pode ver neste guia, configurar as coisas com o Serva requer um pouco de tempo e atenção(time and attention) . No entanto, é a maneira mais simples de instalar qualquer versão moderna do Windows pela rede. Funciona muito bem tanto para redes domésticas quanto para redes empresariais de pequeno ou médio porte.
Se você conhece outras ferramentas úteis para instalar o Windows pela rede, não hesite em compartilhá-las usando o formulário de comentários abaixo.
How to Install Any Version of Windows from Other Network Computers
Talk about a complex thing to do: installing Windows over the network. Eνen installing it via a USB drive is simpler. However, this doesn't mean it cannot be done. Using a free tool nаmed Serva and a bit of time and attention, anyone can set up his/her network environment so that Windows installations are performed with ease, from one network computer. Here's how the whole process works!
VERY IMPORTANT Prerequisites
There are many things you need to prepare beforehand, so that everything works smoothly. Please don't skip any of these elements or the likelihood of failure will be high:
You need to download and extract a little tool named Serva. Download the appropriate version for your operating system (32-bit or 64-bit). You will notice that there are a "Non-Supporter" version and a "Supporter" version. The free one is the "Non-Supporter" version. It includes a small annoyance when you start it, plus a few limitations that won't impact you unless you are a network admin or IT professional who needs to install lots of operating systems on many network computers. If you are such a professional, go ahead and purchase the "Supporter" version which costs a fair $29.99.
"D:SERVA"

You need the original installation files for the operating system(s) you want to install over the network. Have them at hand as you will need to copy them to a special folder, as they are, without modifications.
For the computers where you are about to install Windows over the network, identify their exact network card model(s). Then, download the appropriate drivers for the Windows version you are about to install on them. By default, Windows setup programs support a limited number of network cards. If your system is rather new, then it is very likely that it won't support its network card and the installation procedure will fail.
Every time you run Serva, run it as administrator. This way it has the required permissions to create files, save the settings you make, etc.
When you run Serva, make sure that it is not blocked by your firewall. The application must be set as allowed on the computer where it runs, otherwise it won't be able to transfer anything over the network.
The computer where the installation files are stored and the one where you want to install Windows must be part of the same network. This means that you have a router on your home network, managing network IP addresses and network traffic. If not, then you should directly connect the two computers with a crossover cable.
Step 1 - Run Serva & Make Its Initial Configuration
Run Serva as administrator. The free version will ask you to wait for 7 seconds before you can use it. Once the wait is over, click "Thanks, not today".

Its window is now open. Click Settings.

First, go to the DHCP tab. If your computers are part of the same network and the management of IP Addresses is taken care of by your router, enable these settings: proxyDHCP and BINL.

BINL is a special add-on that acts as a DHCP protocol extension and it is used by Serva during its preparation and maintenance procedures. proxyDHCP is a special setting that tells Serva that it doesn't need to act as a DCHP server in order to provide IP addresses to the computers connecting to it.
Even though Serva's developers don't recommending enabling this setting, we have learned in our testing that it helps eliminate some issues. Therefore, also enable the box which says "Bind DHCP to this address" and leave the default IP address that is provided.

There is no need to modify other settings in this tab. Next, go to the TFTP tab.
TFTP comes from Trivial File Transfer Protocol and it is the protocol used by Serva to transfer files over the network. This protocol needs a bit of configuration as well.
First, check the box near TFTP Server. Then, you need to specify the so called "root" directory. This is the directory where you plan to store the Windows installation files. This folder can be the same folder where you extracted Serva or a new one. Keep in mind that you should use short paths and avoid using spaces and special characters (*, &, ", etc) in the directory name or its path.

To help eliminate problems in some networking environments, you might want to also check the box near "Bind TFTP to this address" and leave the default IP address unchanged.

Press OK to save your settings. Then close Serva and start it again (as administrator). During the restart, it will create a special folder structure in the root folder you specified.

Amongst those folders, you must find one named WIA_WDS and another named WIA_RIS. If they are not found inside the root folder you specified, something went wrong with Serva's configuration. If all is well, go ahead and read the next section in this article.
Step 2 - Copy the Windows Installation Files
Go to the root folder you specified. Here, you need to copy the Windows installation files, as they are, without any modifications from your side.
If you want to install older versions of Windows like Windows XP or Windows 2000, you need to copy those files in the WIA_RIS folder. Since these operating systems are very old and we don't recommend using them, we won't provide specific instructions for them.
If you plan to install Windows Vista, Windows 7 or Windows 8, then open the WIA_WDS folder. There, create a new folder named according to the Windows version you want to copy. Use simple folder names, with no spaces or special characters. For example, I used Windows_7.

Create separate folders, with different names for all the Windows versions you plan to install over the network, using Serva.
Inside that folder, copy and paste all the installation files for the Windows version you want to install over the network. Simply go to the root of the installation disc, and copy its entire file and folder structure.
Step 3 - Start Serva
Start Serva again, as administrator and wait for it to detect the installation files you added. It will create its special folder structure, required to distribute the installation files over the network.
Then, close Serva and go to the next step.
Step 4 - Copy the Network Card Driver(s)
Next, you need to copy the network card drivers for the computer(s) on which you want to install Windows.
Go the folder where you copied the installation files. In my case it was "D:serva" (both the root and Serva installation folder), followed by "WIA_WDSWindows_7".

There, go to "$OEM$$1DriversNIC". If you can't find these folders, create them yourself.
Then, extract the network card drivers and place them inside. If your drivers come as a setup.exe or as a self-extractable archive, extract it first. Make sure the driver's ".inf" and ".cat" files are stored directly in the NIC folder.
Step 5 - Share WIA_WDS Folder with the Network
In order for Serva to distribute the Windows installation files over the network, they need to be shared with the network, so that other computers can access them. Unfortunately, Serva requires you to share the WIA_WDS folder (and not its subfolders or other folders) using a very specific share name: WIA_WDS_SHARE. Using any other share name means that the installation procedure is likely to fail.

To share this folder with the name we mentioned, you first need to enable advanced sharing in Windows and then share it. Here's how advanced sharing works in Windows: Share Libraries or Folders Using Advanced Sharing.
You must give the user Everyone read-only permissions. You can also share this folder with specific user accounts, whose login details you will use later on, during the network installation process. Again, read-only permissions are enough.
Step 6 - Start Serva
Start Serva again, using administrator permissions. It will detect the network drivers you added and make a few changes, so that the drivers are distributed correctly when you launch the installation process on other computers. You can now leave it open and waiting for network connections.
Next, go to the computer(s) where you want to install Windows.
Step 7 - On the Target PC - Enable Lan Booting & Boot from the Network
Go to the computer where you want to install Windows and enter its BIOS. Make sure networking booting is enabled. This setting can be named "Boot from the network" or "Boot from PXE".
Then, start the computer and press the required key to bring up the Boot Menu. On most computers, you need to press F12 or F8, depending on the BIOS version. Select Network or PXE (again, this depends on your computer's BIOS), to boot from the network, using Serva.

If all is well, you should see a screen similar to the one below, where the computer's MAC is displayed and the network card requests an IP address via DHCP.

When the computer is connected to the network, Serva loads and displays a screen with the operating systems available for installation. Pick the one you want and press ENTER.

The installation files are loaded and a small window named ServaPENet is shown. At this step, Serva installs the network driver you added earlier, loads network resources and connects to the Windows installation folder. Depending on how you shared the WIA_WDS folder, it will ask you to provide a username and password to access it. Type the details of the user account you shared it with and connect.
If all went well, the Windows installation process is now started.
Step 8 - Install Windows Over the Network
Next, continue with the Windows installation, as usual. If you plan to install Windows 8, check this installation guide: How to Install Windows 8 RTM on Your Computer.
Troubleshooting Problems with Serva
If you don't pay attention to all the steps in this procedure, some things are likely to fail. Here are some things we learned while experimenting with this tool:
If ServaPENet returns this error: "Failed No NIC/Driver, Aborting!", it means that you forgot to copy the network card drivers as instructed at Step 4. If you copied them and you still get the error, double check that you have the correct driver for the network card of the computer where you want to install Windows, for the Windows version you are about to install. Also, double check that you copied it to the correct folder. Then, restart Serva to make sure it detects the driver before the network installation procedure starts.
If, on the target computer, Serva is not able to load at all over the network, consider enabling the "Bind DHCP to this address" and "Bind TFTP to this address" settings in the DHCP and TFTP tabs.

One last piece of advice is to check the Serva logs. The messages shown there can help you troubleshoot different problems.
Another good tip is to restart Serva every time you change any of its settings and every time you add something to its root folder.
Since we are not the developers of this software, we cannot provide support for it and help you with all the issues you might encounter. If our guide does not help you, then double check Serva's documentation - Serva PXE/BINL - AN01: Windows Install and advanced configuration guide - Advanced Topics on TFTP.
Conclusion
As you can see from this guide, setting things up with Serva requires quite a bit of time and attention. However, it is the simplest way of installing any modern version of Windows over the network. It works great both for home networks and small or medium sized business networks.
If you know other useful tools for installing Windows over the network, don't hesitate to share them using the comments form below.















